Solution
|
|
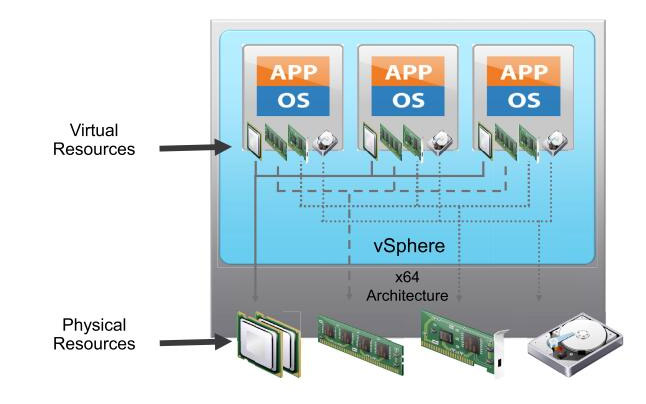
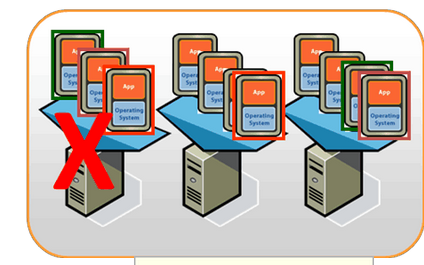
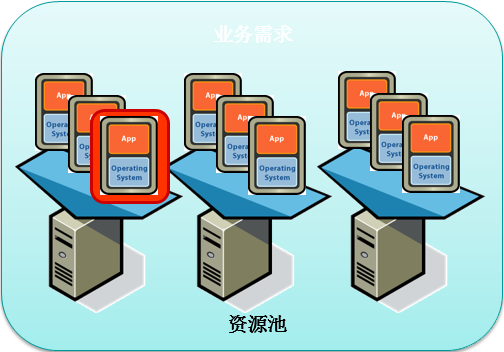
What is virtualization? Simply put, virtualization is the process of creating virtual (rather than physical) versions of certain components. Virtualization can be applied to computers, operating systems, storage devices, applications, or networks. However, server virtualization is the core of virtualization. The current design of x86 servers has limitations, with only one operating system and application running at a time, which poses challenges for IT departments. Therefore, even small data * must deploy a large number of servers, and the capacity utilization of each server is only 5% to 15%, which is very inefficient by any standard. Virtualization uses software to simulate hardware and create virtual computer systems. In this way, enterprises can run multiple virtual systems on a single server, that is, multiple operating systems and applications, which can achieve economies of scale and improve efficiency. Utilizing VMware's virtualization platform, VMware vSphere ® With Operations Management ™ Integrating server hardware can eliminate excessive configuration, improve server utilization, and limit the impact of IT on the environment.
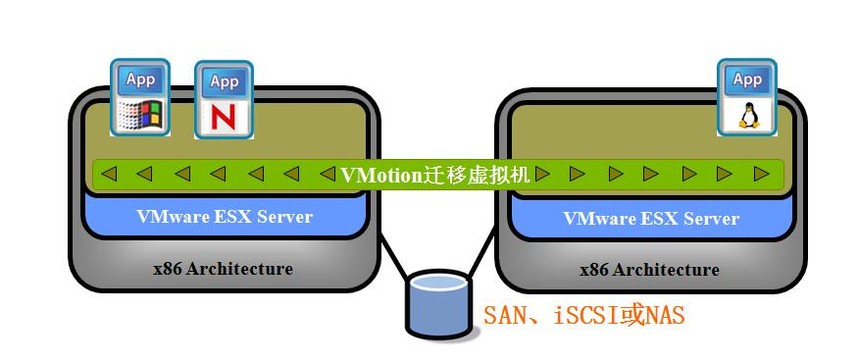
Through server integration, your company can: 1.1 Reduce hardware and maintenance costs by up to 50%, and energy costs by up to 80%. 1.2 Reduce the time required to provision new servers by up to 70%. 1.3 Reduce downtime and improve reliability by leveraging business continuity and built-in disaster recovery capabilities. 1.4 Provide IT services on demand, eliminating reliance on hardware, operating systems, applications, or infrastructure providers. VMOTION Function: VMware VMotion enables dynamic migration of virtual machines without service interruption Advantages: Zero downtime: Planned workstation maintenance, upgrades, and migration of workloads to maximize resource utilization Continuous availability of workstations, complete transaction integration Supports Fiber Channel and iSCSI-SAN environments as well as NAS
VMware HA(High Availability) Function: Automatically start a new virtual machine when the server fails Advantages: High availability and low cost for all applications No need for completely consistent repetitive hardware Compared to traditional clusters, it has a higher cost advantage while being easy to use and operate No need to purchase 2 sets of operating systems, dual machine software Traditional HA may sometimes encounter issues with unsuccessful switching
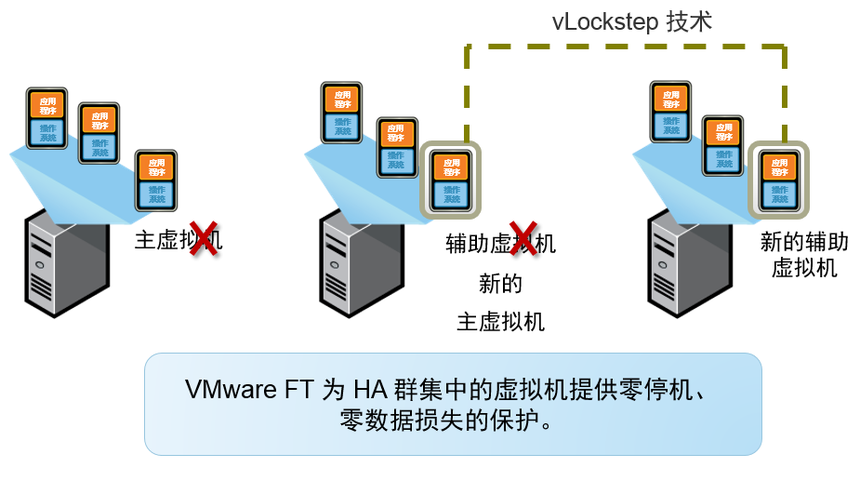
VMware Fault Tolerance (FT) Real time monitoring of virtual machine operation status to ensure automatic restart of another virtual machine in case of virtual machine error
VMware Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS) function Dynamic adjustment of computing resources across resource pools Intelligent resource allocation based on predefined rules advantage Align IT and business priorities Dynamically improving system management efficiency Automated hardware maintenance
|